Epistaxis
This policy applies to: Patients whose chief complaint is severe or prolonged bleeding from the nose.
Exclusion Criteria: Patients with respiratory compromise may first require airway control and mechanical ventilation. Patients with hemodynamic compromise may first require volume and blood product resuscitation.
Recognize
- Severity of Bleeding
- Airway patency
- Distress or Anxiety
- Blood Thinners / Coagulopathies
- Hemodynamic status
- Facial trauma
- Environmental factors
Evaluate
- Medical History and Medications
- Airway patency
- Circulatory status
- Bleeding disorders
- Estimate Blood Loss
- Pain
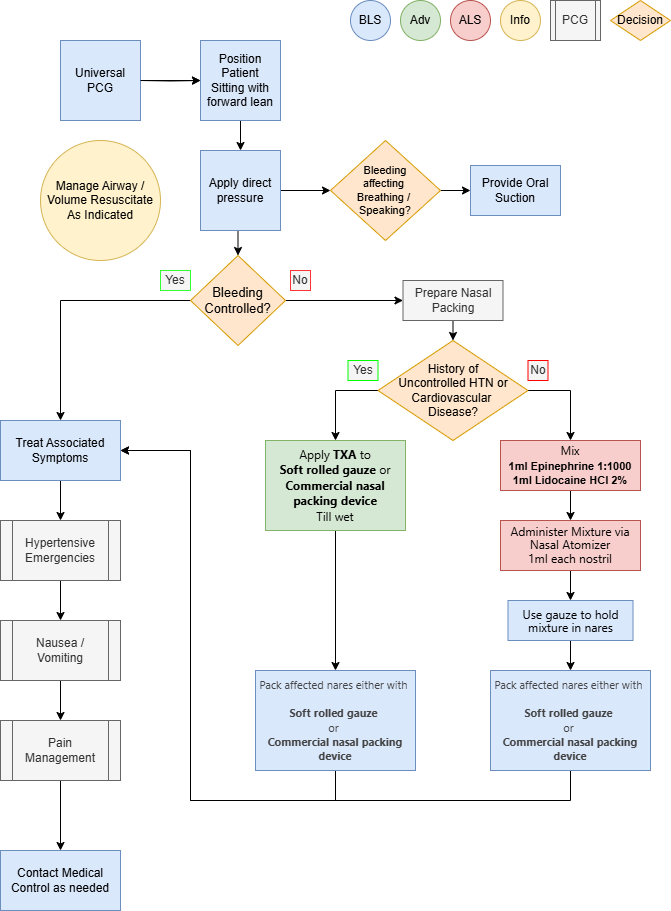
Administer Treatment
- Patient positioning
- Place patient in an upright sitting position with a forward lean to prevent ingestion or aspiration of blood.
- Apply direct pressure to the soft part of the nose.
- Provide oral suctioning as needed.
- Manage hypovolemia / shock as indicated.
- Manage airway as indicated
- Consider Zofran IV/IO for nausea associated with blood ingestion. Avoid PO administration.
- Consider analgesia.
- Consider mild sedation due to risk of increased bleeding from anxiety associate hypertension.
- If bleeding unresolved via direct pressure consider nasal packing.
- Prepare mixture of:
- 1ml Epinephrine 1:1000
- 1ml Lidocaine HCl 2%
- For patients with Cardiovascular disease or uncontrolled hypertension:
- Apply TXA as needed to soft rolled gauze or a commercial nasal packing device till wet.
- Begin packing affected nares.
- For all else:
- Administer 1ml of mixture to each affected nare via nasal atomizer. Using gauze to prevent leaking after administration.
- Begin packing affected nares either with moistened soft rolled gauze or a commercial nasal packing device.
- Administer 1ml of mixture to each affected nare via nasal atomizer. Using gauze to prevent leaking after administration.
- Consider IV/IO opioids for pain management. Avoid PO administration.
- Prepare mixture of:
Consider Differentials
- Facial Fractures
- Uncontrolled Hypertension
- Illicit drug use
- Bleeding Disorders
Navigate
References
Protocols
Medications
Procedures
Resources
