Hypoglycemia
Applies to: Patients with blood sugar < 60 mg/dl
Exclusion Criteria: None
Recognize
- Altered mental status
- Anxiety
- Slurred speech
- Sweating
- Pale skin
- Tremors
- Seizures
- Medic alert bracelet / jewelry
Evaluate
- Primary survey with airway management
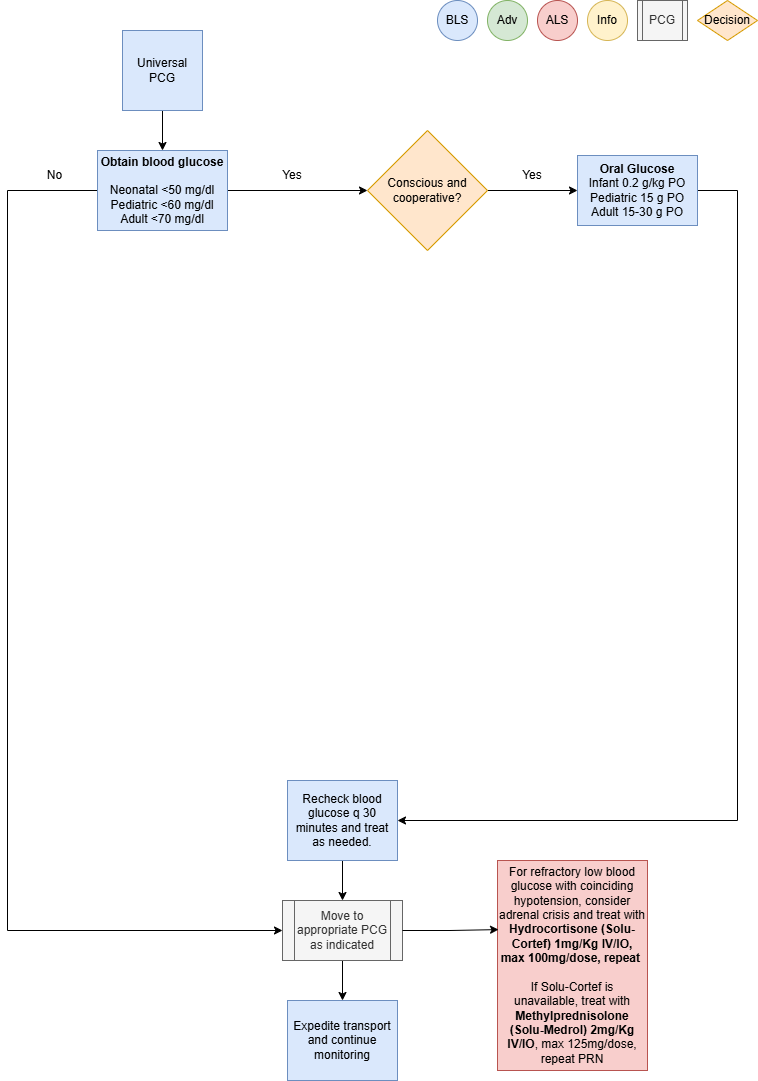
- Obtain blood glucose measurement
Administer Treatment
- If patient has altered mental status with concerns of inability to protect airway, obtain IV access,
reference Vascular Access (P33) - Supplemental oxygen PRN for goal SpO2
- Adult: treat patients with a blood glucose reading of < 70 mg/dl
-
- If patient is conscious, cooperative and can protect their airway, administer Oral Glucose 1-2
tubes (15-30g) PO - If patient has altered mental status or there is concern of inability to protect airway,
administer D10W, 125 mL (12.5 gm) IV/IO over 10 minutes, may repeat PRN-
- If D10W is not available, administer Dextrose 50%, 25-50mL (12.5-25 gm) IV/IO over
5 to 10 minutes, may repeat PRN
- If D10W is not available, administer Dextrose 50%, 25-50mL (12.5-25 gm) IV/IO over
-
- Consider Glucagon 1mg IM (>20 Kg patients) if venous access unobtainable
- If patient is conscious, cooperative and can protect their airway, administer Oral Glucose 1-2
-
- Repeat blood glucose measurement every 30 minutes and treat accordingly
- For persistent hypoglycemia despite treatment, consider a maintenance infusion with escalating
dextrose concentration-
- D12.5% is the highest dextrose concentration that may be infused peripherally
- Dextrose concentrations higher than D12.5% require a central line or IO
-
- For refractory low blood glucose with coinciding hypotension, consider adrenal crisis and treat with
Hydrocortisone (Solu-Cortef) 1mg/Kg IV/IO, max 100mg/dose, repeat PRN-
- If Solu-Cortef is unavailable, treat with Methylprednisolone (Solu-Medrol) 2mg/Kg IV/IO,
max 125mg/dose, repeat PRN
- If Solu-Cortef is unavailable, treat with Methylprednisolone (Solu-Medrol) 2mg/Kg IV/IO,
-
Consider Differentials
- Environmental exposure
- Toxic ingestion
- Alcoholism
- Sepsis
- Metabolic etiology
- Adrenal crisis
Transport Considerations
- Blood glucose measurement is required on all patients less than 1 year of age, if not obtained at
sending facility within the last 4 hours - Hypoglycemia and hypothermia often coexist. If one of these conditions exists, determine if the
other is also present
Information
- Hypoglycemia should be considered in any person with an altered LOC. However, glucose should not
be administered unless the patient is actually hypoglycemic. Administration of glucose or dextrose to
a patient who does not have hypoglycemia but instead has experienced a stroke resulting in an
altered LOC could be detrimental - Remember that sick children have high metabolic requirements with high glucose utilization. Check
blood glucose early and often - D10W is the preferred IV bolus solution to treat hypoglycemia
- Abnormal glucose levels to be considered hypoglycemia and treated during transport:
-
- Adult < 70 mg/dl
- Pediatric < 60 mg/dl
- Neonatal < 50 mg/dl
-
Other Populations
- Neonate and Pediatric Dosing:
-
- Oral Glucose 0.2g/Kg PO (infant), 15g PO Pediatric
- D10W, 2mL/Kg slow IV/UVC/IO over 10 minutes, may repeat PRN
- Glucagon 0.5 mg IM (<20 Kg) or 1mg IM (>20 Kg) if venous access unobtainable
-
- Neonate:
-
- Hypoglycemia has the potential for causing severe neurological damage
- Symptoms manifest mostly from CNS (jittery, high pitch cry, seizures)
- High glucose utilization may quickly deplete glycogen stores resulting in persistent hypoglycemia
- Consider Inborn Error of Metabolism, specifically medium chain fatty acid deficiency (MCAD), in neonates with persistent hypoglycemia
-
Navigate
References
De Leon-Crutchlow, Diva D., et al. "Approach to Hypoglycemia in Infants and Children." UpToDate, Jul 2021.
“U.S. Army Medevac Critical Care Flight Paramedic Standard Medical Operating Guidelines.” Jan 2020.
Vella, A., et al. "Hypoglycemia in Adults without Diabetes Mellitus: Clinical Manifestations, Diagnosis, and
Causes." UpToDate, Feb 2021.
